Bedside Barcoding
Bedside Barcoding
No one intends to make a serious medication error. But more than 7,000 Americans die each year when clinicians improperly prescribe, transcribe, process, or administer medications.[1] Harmful medical errors are estimated to occur in 1-10% of patients.
Most of these medication errors originated during the prescriber ordering and nurse administration phases of the medication process. The findings of these medication error studies that show the majority of medication errors occur at the patient bedside which is 38%.
The nurse then scans patient's bracelet ( barcoded), The Patient's medication record will appear. It is matched with a barcode on medication that is prescribed specifically for the person.
How it works
Patient is assigned a bracelet that contains an assigned barcode that usually consisits of their Hospital number.
When medication is ordered, it gets sent to the computerized pharmacy system for verification by the pharmacist.
The nurse scans their barcode name badge and enters password.
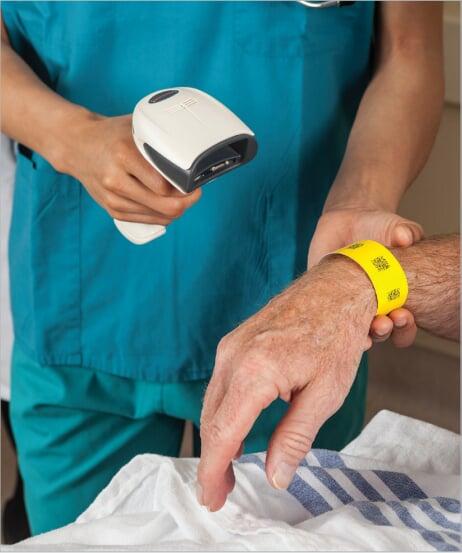
The nurse then scans patient's bracelet (barcoded), The Patient's medication record will appear.
The nurse then scans the packaged medication before administration to check that the medication is for right patient, the dose is right, and the time for the dose is correct.
An Electronic Record is automatically produced.
Advantages
Accurate documentation of medication administrated (Who, When , What)
Reduced medical errors
Provides positive identification
Disadvantages
Time consuming
Training Costs
References
1. Kohn L., Corrigan J., and Donaldson, J. (eds.):To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System. Washington, D.C., National Academy Press, 1999.

